For those who are affected by severe obesity, Bariatric surgery is proven to be a safe and effective treatment option. It is currently the only treatment available that can provide a significant and sustained weight loss. Bariatric surgery also has an impact on hormonal and metabolic changes that play a major role in your desire to start eating and your desire to stop eating. Not only does bariatric surgery result in significant weight loss, but it can also decrease the risk of having many conditions that occur as a result of severe obesity, such as heart disease, gastroesophageal reflux disease, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, severe sleep apnea, and a stroke.
There are four main types of bariatric surgery. Choosing which one is best for you can be difficult, especially if you don’t know the difference between each one. In this article, we’ll explain everything you need to know about the four main types to help you determine the best option for you.
Gastric Bypass
Gastric bypass is currently the most common type of bariatric surgery. With gastric bypass, a small pouch is created from the stomach and connected directly to the small intestine. After the surgery, food will bypass most of your stomach because they go into the small pouch and directly to the small intestine. The surgery is irreversible.
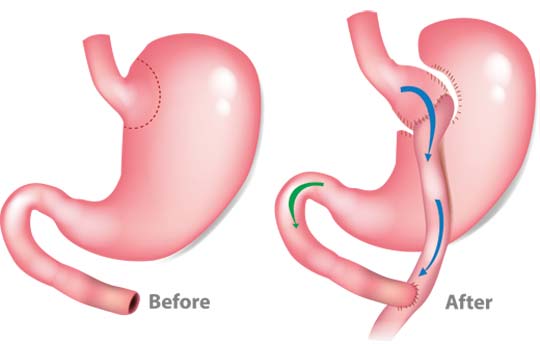
Gastric bypass is known to provide long-term weight loss. However, the amount of weight you lose depends on the change to your lifestyle habits. There are some restrictions and limits on how much and what you can consume after the surgery. If you follow these restrictions and change your lifestyle, you may be able to lose 60% of their excess weight within two years. Some people even lose more than 60%, while others will lose less.
Although the procedure is done to treat severe obesity, not everyone can undergo the procedure. There are certain medical guidelines you need to meet to qualify for gastric bypass surgery. In general, gastric bypass can be performed on people whose body mass index (BMI) is 40 or higher (extreme obesity) as well as those whose BMI is 35 to 39.9 (obesity) and suffer from a serious weight-related medical condition, such as high blood pressure and type 2 diabetes. In some cases, if your BMI is 30 to 34 and you have serious weight-related problems, you also qualify to undergo the surgery.
You need to be aware of the risks of gastric bypass. These risks include pouch stretching (your stomach stretches back to its original size), breakdown of staple lines, nutritional deficiency, and stomal stenosis. Some people experience “dumping syndrome,” which is a condition where food moves too quickly from your stomach to the small intestine and cause weakness, nausea, sweating, or diarrhea after eating.
Gastric Sleeve
With Gastric sleeve surgery, a portion of your stomach is removed to reduce its size to about 15% of its previous size. Your new stomach will be shaped like a banana or a sleeve. With just a small part of your stomach left, you will feel full a lot quicker than you used to and you will not be able to eat as much as you did before and as a result, your weight will be reduced. After a gastric sleeve, your body’s ability to produce a hunger hormone called ghrelin is reduced.
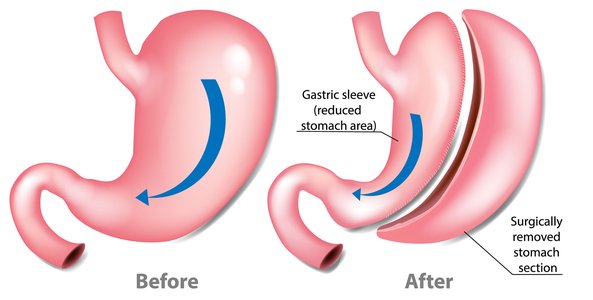
Gastric sleeve is an irreversible procedure and you may need to stay in the hospital for 2 to 3 days after the surgery. You will only be allowed to drink clear liquids the first day after surgery. For about four weeks after the surgery, you can only consume protein shakes and pureed foods.
What you need to remember is that you will need to change the way you eat forever. You can start eating soft solid food after a month, but you must chew everything thoroughly before swallowing, wait for a half-hour to drink liquid after a meal, and avoid high-calorie sodas. After three months, you should be able to eat regular meals but you will not be able to eat as much as you used to. You may not be able to eat certain foods.
Most people who have had a gastric sleeve generally loose around 60% of their extra weight after 12 to 18 months. So you will lose approximately 60 pounds if you are 100 pounds overweight. However, some people can lose more than 60%, while others lose less.
The risk of a gastric sleeve includes infection, bleeding, and a leak along with the stitches. The side effect you need to be aware of is nutrition problems, which is why you may need to take supplements and vitamins.
Gastric Band
Unlike gastric bypass and gastric sleeve, a gastric band is quick, minimally invasive, reversible, and adjustable. The procedure involves placing an adjustable silicone band on the upper part of your stomach to reduce the stomach size. This silicone band will squeeze the stomach so it becomes a pouch. A tube is attached to the band to adjust the band. This tube can be accessed through a port under the skin of your abdomen.
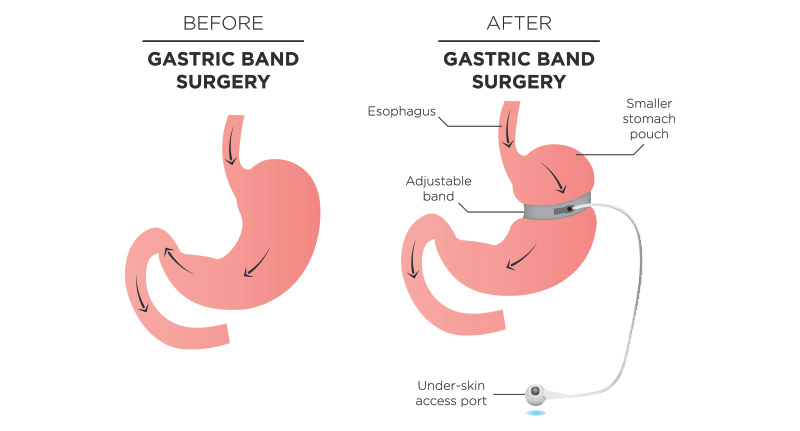
In the past, the gastric band could only be performed if your BMI was 35 or above. People with BMI between 30 and 34.9 could only undergo this surgery if they had weight-related medical problems, such as sleep apnea, hypertension, and diabetes. These guidelines were made due to the risk of complications. However, advancements in surgical techniques have greatly improved the safety of gastric band surgeries. Those with a BMI of 30 – 35 can also undergo this surgery if non-surgical approaches have not proven effective and if they have weight-related conditions.
You can generally lose between 40% and 60% of excess weight, but this will be different from one person to another. You will need to follow the dietary recommendations from your doctor. You should also avoid overeating because it can lead to esophagus dilation and vomiting.
A gastric band is known to have less risk than gastric sleeve and gastric bypass. However, one of the disadvantages of a gastric band is that progress may be slower compared with other types of bariatric surgery. Another risk to bear in mind is that the band can have mechanical problems or slip, which would require removal.
Gastric Balloon
Gastric Balloon is one of the newest types of bariatric surgery. Just like a gastric band, it is also minimally invasive, and reversible. This procedure involves putting a saline-filled silicone balloon in your stomach to obstruct a sizable area of your stomach, which will then reduce the amount of food you can eat at any one time. The balloon is typically removed using an endoscope within 6 months.

The procedure is ideal for people with a BMI of 30 – 40. It may not be suitable for everyone, so your doctor will perform a screening process to see if it will be beneficial for you. Like other bariatric surgeries, you need to commit to a healthy lifestyle after a gastric balloon. You will also need to take vitamins, supplements, and minerals regularly.
You can expect to lose about 10% to 15% of your excess weight during the six months after gastric balloon placement. If you combine the procedure with behavioral therapy, you may be able to lose 29% of your excess weight. The result of a gastric balloon may not be as high as other bariatric surgery, but it is known to be safer. Serious risks are very rare and most people only experience pain and nausea, but these only last for a few days and can be managed with oral medication.